August 2025
Announcing Rsdoctor 1.2
Rsdoctor 1.2 has been released! 🎉
- Deep concatenated module analysis: Added the ability to analyze the size of concatenated modules, helping developers more accurately identify the actual build size after Tree Shaking.
- Bundle Size Analysis with Gzip Support: Bundle size analysis now displays the size after gzip compression, making it easier for developers to understand the real size of production assets.
- Enhanced Treemap Visualization: Introduced and improved the Treemap (rectangle tree map) feature, allowing developers to gain more intuitive insights into bundle composition and resource distribution.
- Rsdoctor MCP: Rsdoctor MCP is an LLM-powered build analysis tool that helps developers quickly obtain build analysis results through Q&A interactions.
Deep concatenated module analysis
During the Rspack build process, certain modules are hoisted or aggregated into a single closure, forming a concatenated module to improve browser execution efficiency and reduce artifact size. Previously, Rsdoctor could not further decompose and analyze the internal structure of these concatenated modules, as they cannot be further split through AST parsing.
Rsdoctor 1.2 supports the ability to analyze concatenated module sizes, helping developers accurately understand the actual build size of sub-modules (aggregated modules) after tree shaking and compression, facilitating analysis of how concatenated modules affect final bundle size and optimization of code splitting strategies.
Additionally, the Rsdoctor plugin built into Rspack (>=1.4.11) has enhanced source map capabilities, allowing seamless analysis of concatenated modules without enabling source maps. However, Webpack projects still require source maps to be enabled.
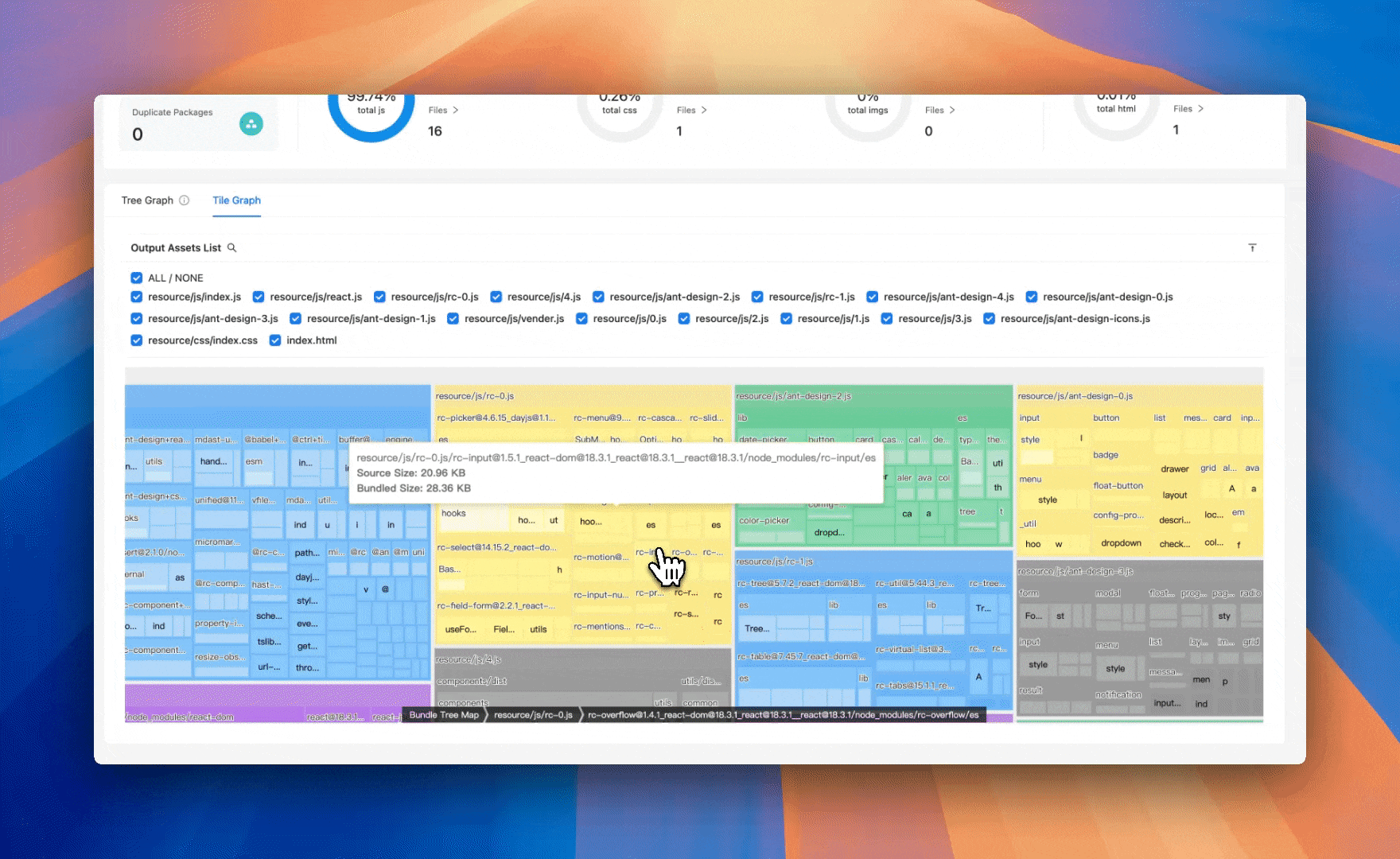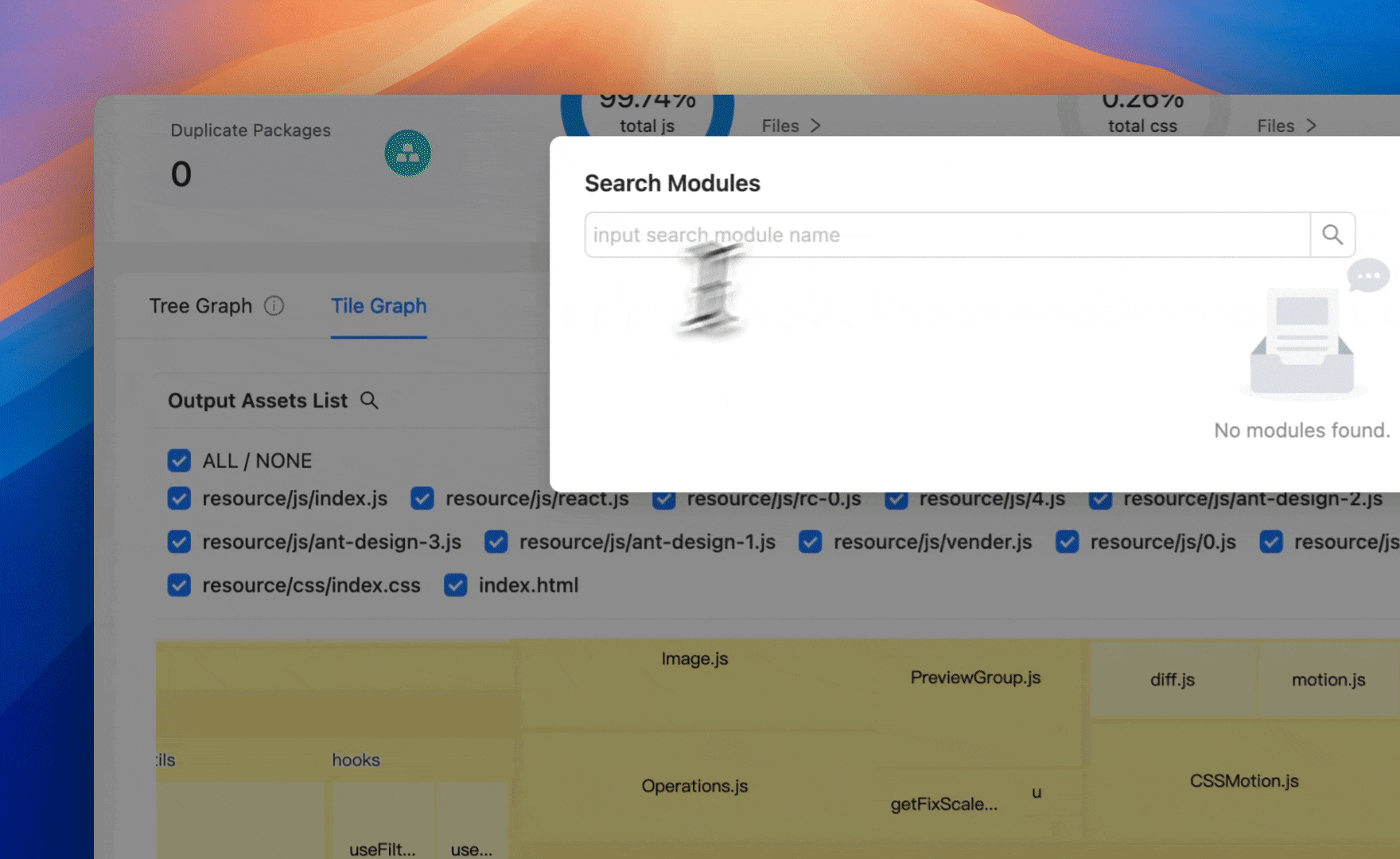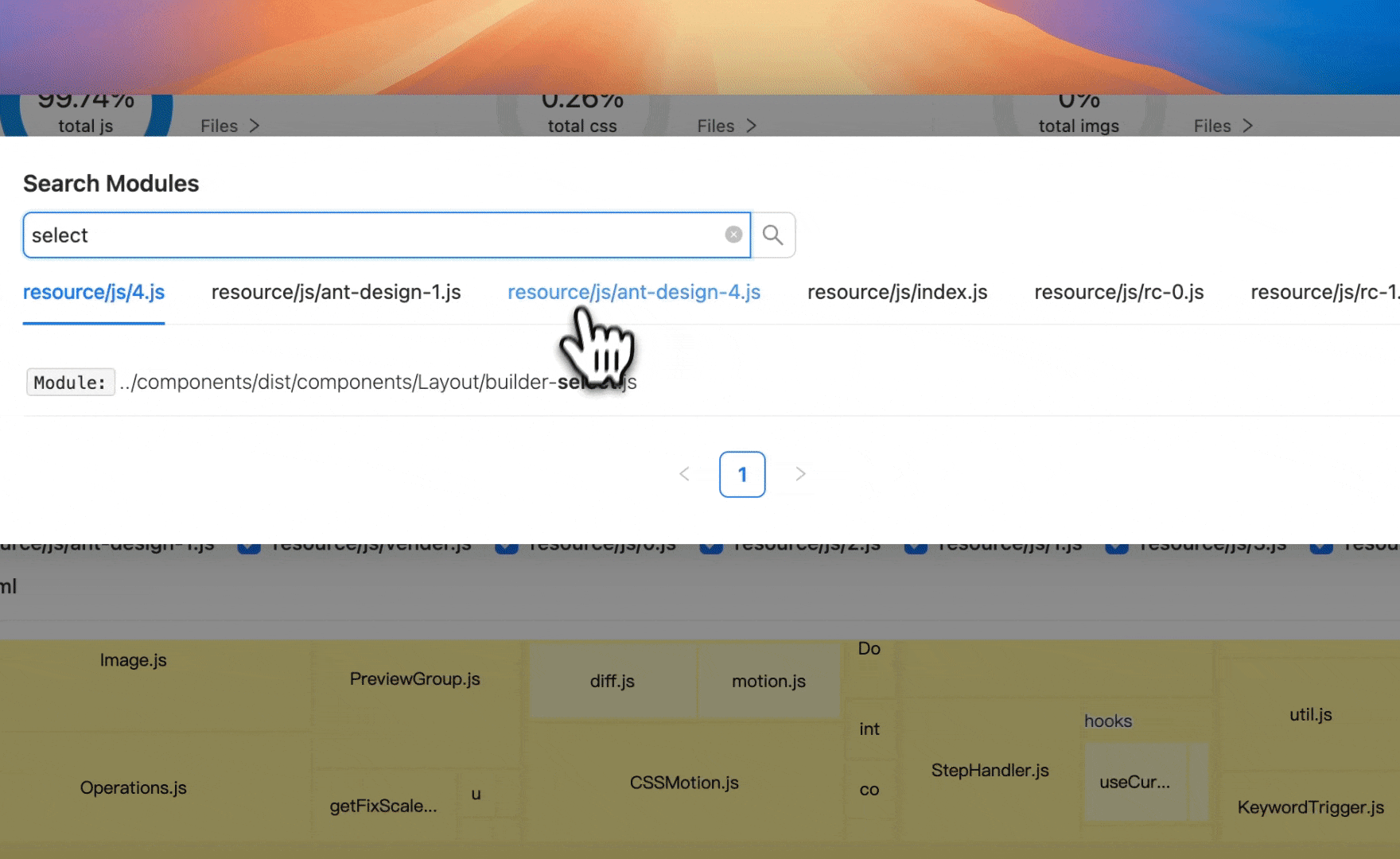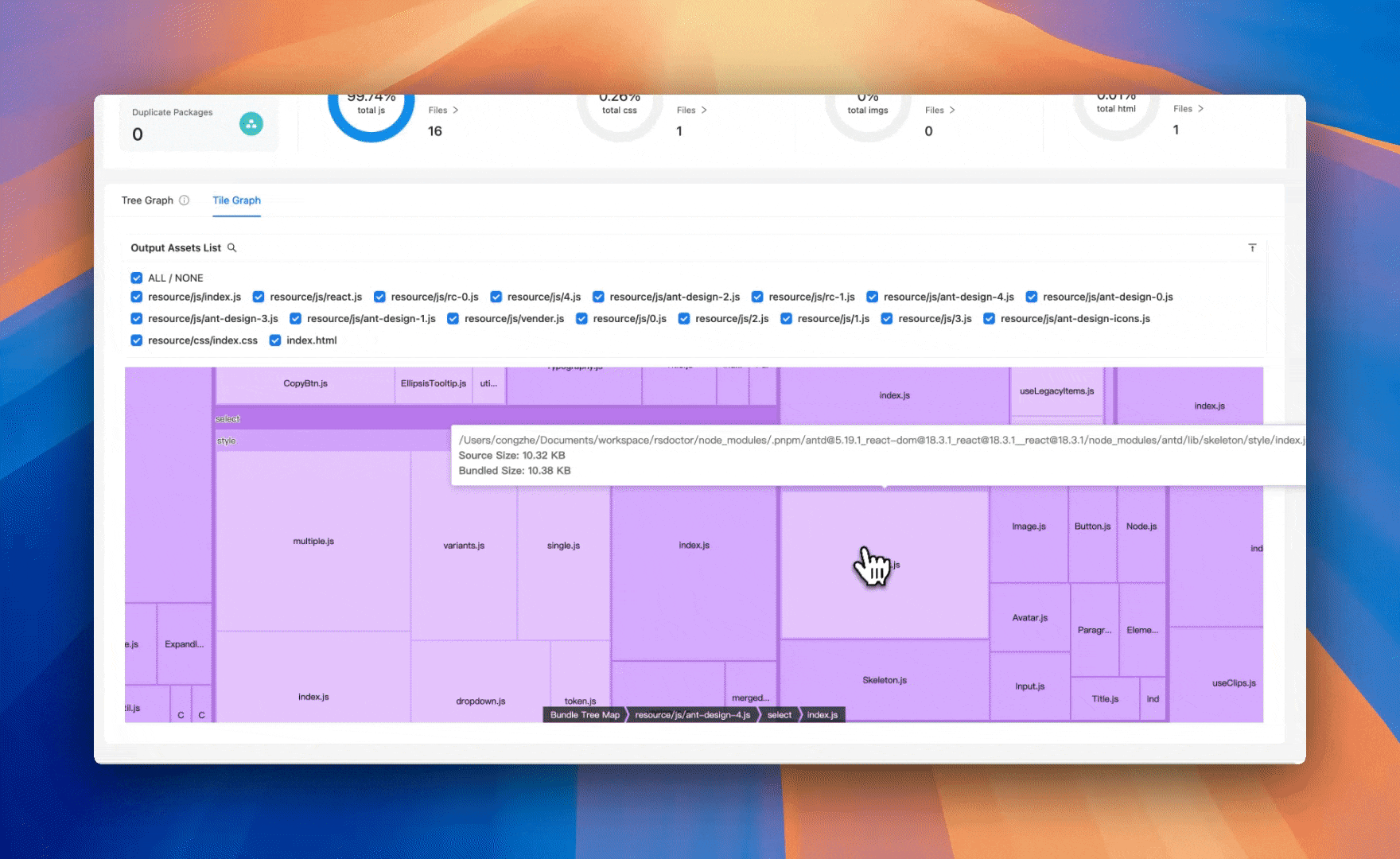
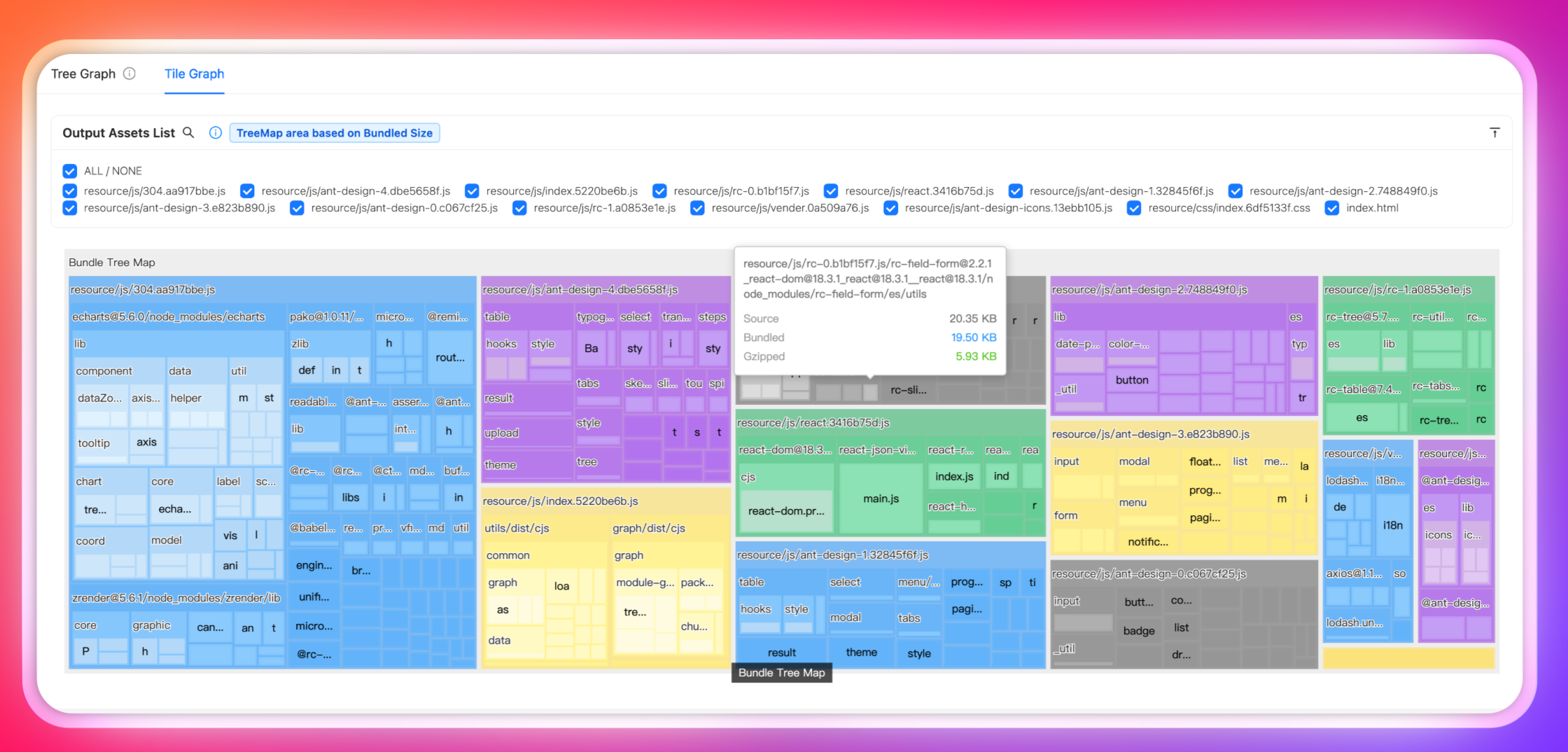
Enhanced treemap visualization
Previously, Rsdoctor's Treemap view was implemented based on webpack-bundle-analyzer, which required Rsdoctor to go through webpack-bundle-analyzer's processing pipeline again after completing its analysis, reducing overall analysis efficiency. Additionally, Treemap page loading was slow, while Treemap is precisely the most commonly used visualization view for developers when analyzing bundles.
Rsdoctor 1.2 introduces a new classic Treemap artifact analysis view, helping developers more intuitively visualize and analyze bundle composition, Assets, and Modules proportions. You can also search for module resources, click on the module resource, and zoom in to the module area.
Support gzip size
To more accurately reflect production environment size performance, Rsdoctor has added support for analyzing gzip compressed sizes, which can be viewed on the Bundle Size page and TreeMap page, as shown below:
This shows a comparison between original size and gzip compressed size, providing more accurate reference data for production environment optimization.
Rsdoctor MCP
Rsdoctor provides rich build analysis data, but developers need to spend time on page interactions and learning costs to perform build analysis and optimization. Therefore, we hope to leverage LLM for more intelligent build analysis to help users obtain analysis results more quickly.
Rsdoctor v1.1 introduced MCP support, which is based on Model Context Protocol (MCP) protocol, combining Rsdoctor's analysis capabilities with LLM's intelligent understanding abilities. Through natural language Q&A interactions, developers can quickly obtain build analysis results without needing to deeply understand complex analysis interfaces and data structures. Its main features include obtaining artifact information, dependency analysis, optimization suggestions, compilation performance, and tree shaking analysis among other core analytical capabilities.
Rsdoctor MCP supports natural language Q&A - you can directly ask questions like "Which packages have the largest volume?" or "Why wasn't this module tree-shaken?" The system will intelligently analyze and provide optimization suggestions, helping you quickly identify and resolve build issues.
In addition, the 1.1-1.2 versions also included other capability changes. For complete update details, please refer to: Release page

